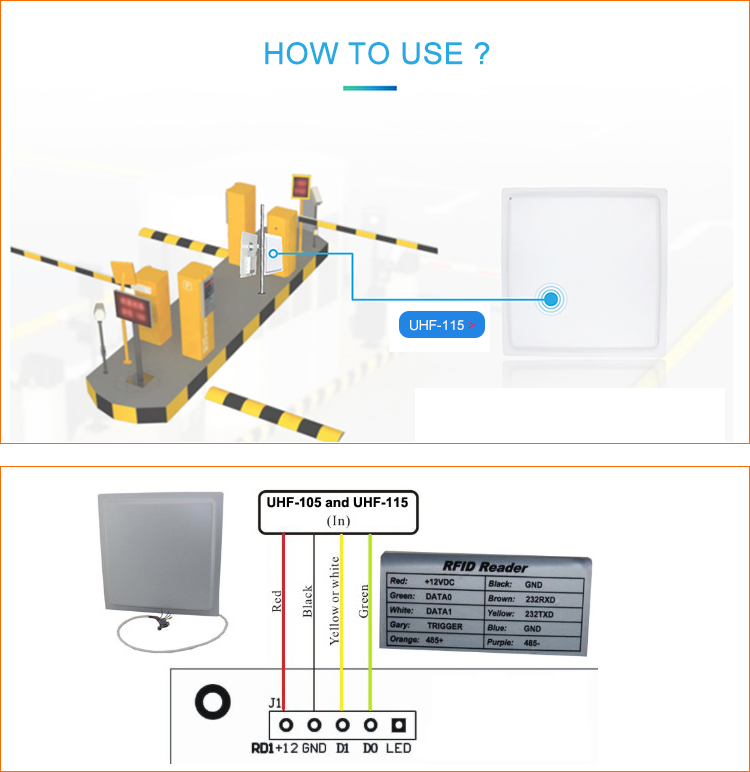
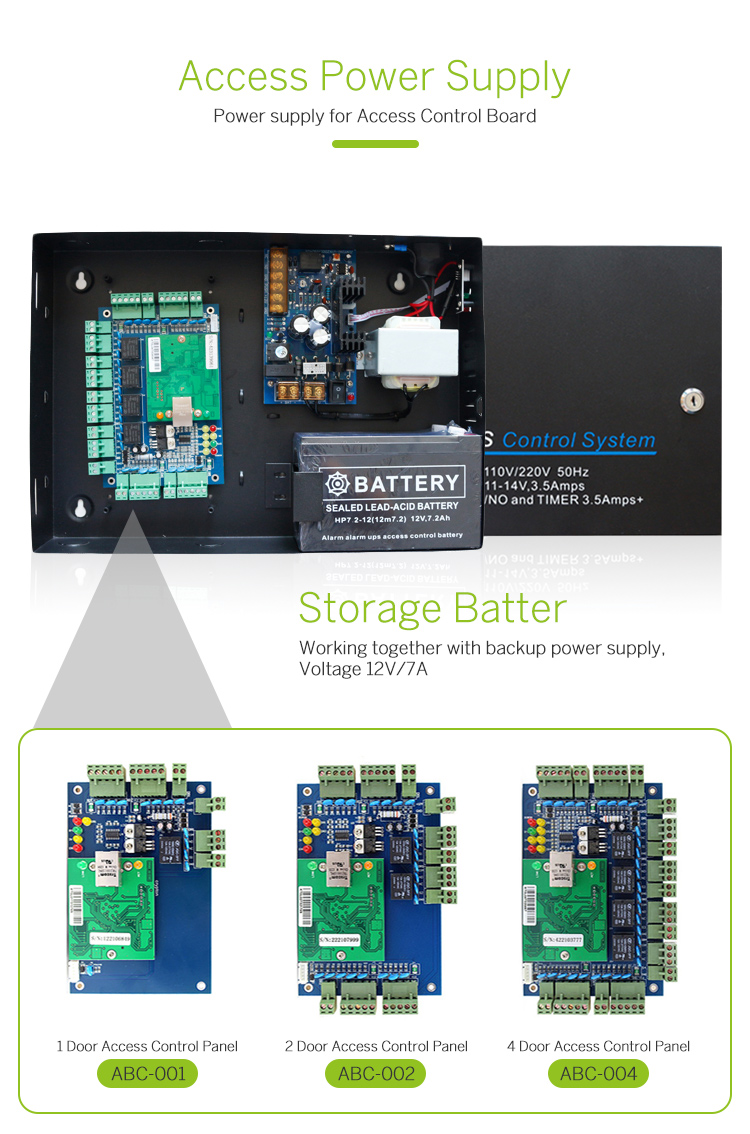
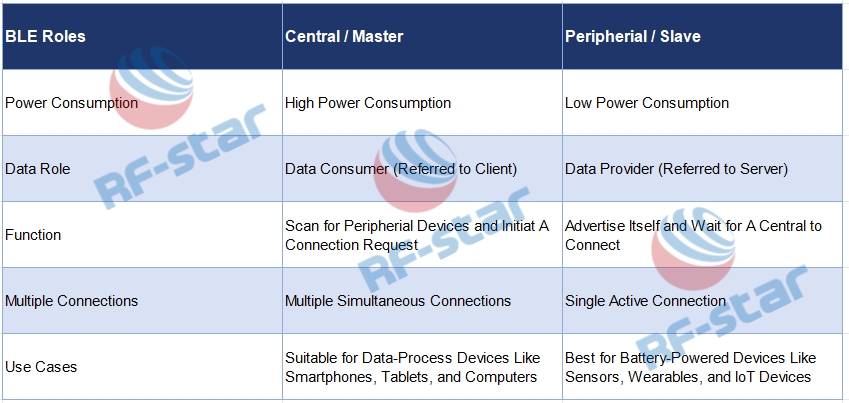
OTDR The Backbone of Optical Fiber Network Maintenance
In the fast-paced digital era, where communication relies heavily on data transmission through optical fiber networks, maintaining the integrity and efficiency of these networks is paramount. Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) is a crucial tool used in the maintenance and troubleshooting of these networks. This article explores the significance of OTDR in ensuring seamless communication and discusses its functions, advantages, and common applications.
OTDR, short for Optical Time Domain Reflectometer, is a specialized instrument used to characterize and troubleshoot optical fiber networks. It works on the principle of sending optical pulses into the fiber and analyzing the reflected light to determine various parameters such as loss, attenuation, and distance.
Key Functions of OTDR:
1 Optical Fiber Fault Detection: OTDR helps in locating and identifying faults, such as fiber breaks, bends, or excessive losses along the fiber optic cable. By analyzing the time and intensity of the reflected light, it accurately pinpoints the exact location of the fault.
2 Fiber Length Measurement: OTDR measures the length of the fiber optic cable accurately. This information is crucial for estimating the overall distance covered by the cable and ensuring proper network planning.
3 Fiber Attenuation Measurement: By analyzing the strength of the reflected light, OTDR can determine the amount of signal loss (attenuation) experienced by the optical fiber. It helps in assessing the overall health and performance of the network.
4 Fiber Characterization: OTDR provides a comprehensive analysis of the optical fiber characteristics, including the splice loss, connector loss, and nonlinear effects. This information enables technicians to optimize the network's performance and identify potential issues.
Advantages of OTDR:
1 Precision and Accuracy: OTDR offers high precision and accuracy in measuring parameters such as loss and distance, providing reliable data for network analysis.
2 Time Efficiency: By combining multiple functions in a single instrument, OTDR saves time and effort in network troubleshooting and maintenance.
3 Non-Destructive Testing: OTDR performs non-destructive testing, meaning it does not interfere with normal network operations when examining the optical fiber cable.
Common Applications of OTDR:
1 Network Installation and Maintenance: OTDR plays a crucial role in network deployment, verifying proper installation and ensuring the fiber's integrity and performance.
2 Fiber Optic Link Characterization: OTDR helps in characterizing optical fiber links by measuring the fiber length, attenuation, and identifying potential issues such as high splice or connector losses.
3 Fault Location and Troubleshooting: OTDR assists technicians in locating and diagnosing fiber optic faults, reducing downtime and improving network reliability.
4 Fiber Network Upgrade and Expansion: OTDR is used to assess the viability of installing additional network equipment and expanding the existing fiber infrastructure.
In today's interconnected world, where optical fiber networks form the backbone of communication systems, the role of OTDR in network maintenance cannot be understated. By accurately detecting faults, measuring distances, and characterizing fiber links, OTDR ensures the smooth operation and optimal performance of these networks. Its precision, efficiency, and versatile applications make it an indispensable tool for technicians involved in optical fiber network maintenance.
sr